|
Principle of the assay:
The test is an enzyme-immunoassay based on a 'sandwich' principle.
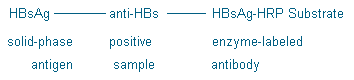
Polystyrene microtiter strip wells have been coated with hepatitis B surface antigen, which constitutes the solid-phase antigen. The test sample is incubated in such a well; anti-HBs, if present in the sample, will bind to the solid-phase antigen. In the mean time HBsAg, which has been labeled with the enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP), is added. With a positive reaction, solid-phase antigen/anti-HBs/HBsAg-HRP complex has been formed. Incubation with enzyme, hydroperoxide and TMB produce a blue color in the microwell, which turns yellow when the reaction is stopped with sulfuric acid. If the sample contains no anti-HBs, then the labeled antigen can not be bound specifically and only a low background color develops.
|